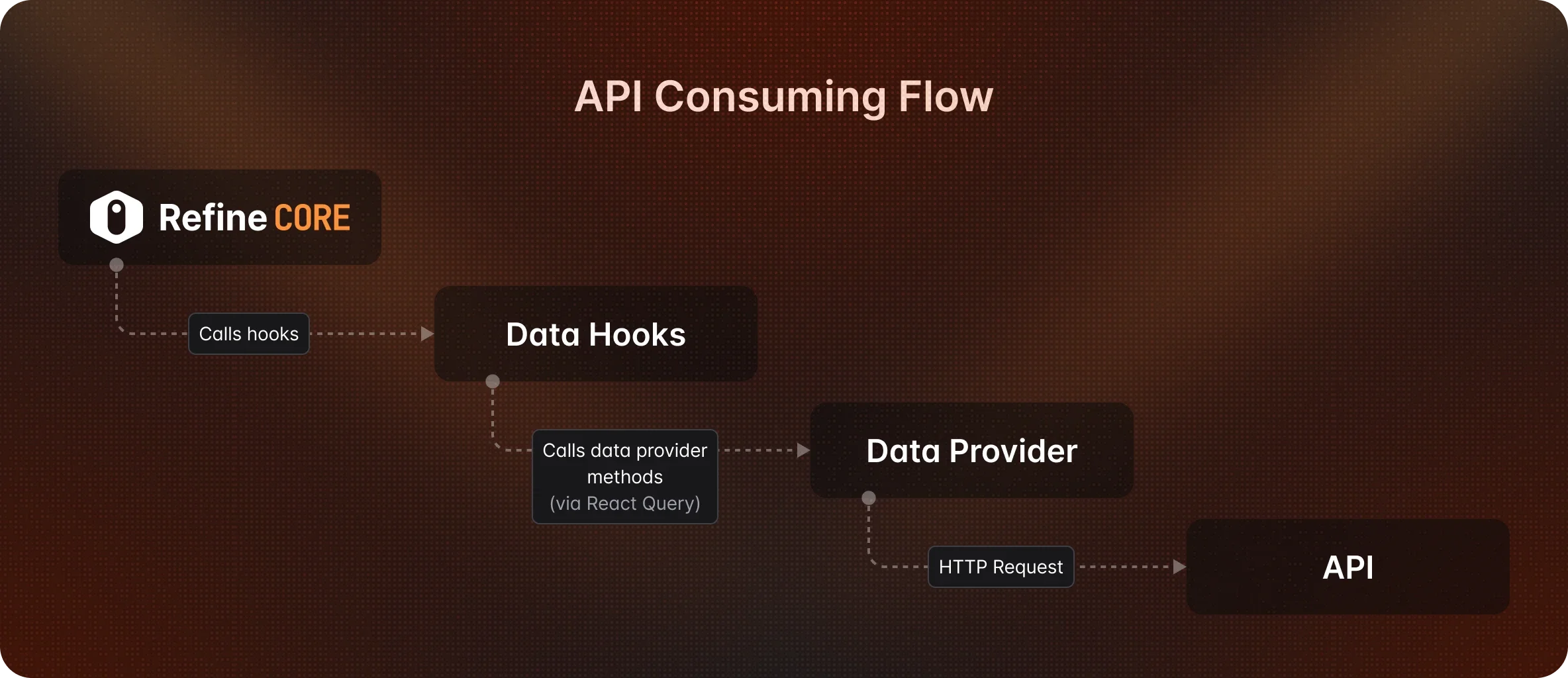
Data Provider
The data provider acts as a data layer for your app that makes the HTTP requests and encapsulates how the data is retrieved. refine consumes these methods via data hooks.
You don't need to worry about creating data providers from scratch. refine offers built-in data provider support for the most popular API providers. So you can use one of them or you can create your own data provider according to your needs.
NOTE
Data hooks use TanStack Query to manage data fetching. It handles important concerns like caching, invalidation, loading states, etc.
Usage
To activate the data provider in refine, we have to pass the dataProvider to the <Refine /> component.
import { Refine } from "@pankod/refine-core";
import dataProvider from "./dataProvider";
const App: React.FC = () => {
return <Refine dataProvider={dataProvider} />;
};
Refer to the Data Provider tutorial for more information and usage examples →
Multiple Data Providers
refine gives you the ability to use multiple data providers in your app. All you need to do is to pass key, value pairs to the dataProvider prop of the <Refine /> component in a form of value being the data provider and the key being the name of the data provider.
Here is an example of using multiple data providers in your app:
CAUTION
default key is required for the default data provider and it will be used as the default data provider.
const App = () => {
return (
<Refine
dataProvider={{
default: defaultDataProvider,
example: exampleDataProvider,
}}
/>
);
};
You can pick data providers in two ways:
- Using
dataProviderNameprop in the data hooks and all data-related components/functions.
useTable({
dataProviderName: "example",
});
- Using
options.dataProviderNameproperty in your resource config
This will be the default data provider for the specified resource but you can still override it in the data hooks and components.
const App = () => {
return (
<Refine
dataProvider={{
default: defaultDataProvider,
example: exampleDataProvider,
}}
resources={[
{
// **refine** will use the `default` data provider for this resource
name: "posts",
},
{
name: "products",
options: {
// **refine** will use the `exampleDataProvider` data provider for this resource
dataProviderName: "exampleDataProvider",
},
},
]}
/>
);
};
Methods
Data provider's methods are expected to return a Promise. So, you can use these async methods to create a data provider.
import { DataProvider } from "@pankod/refine-core";
const dataProvider: DataProvider = {
// required methods
getList: ({ resource, pagination, hasPagination, sort, filters, metaData }) =>
Promise,
create: ({ resource, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
update: ({ resource, id, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
deleteOne: ({ resource, id, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
getOne: ({ resource, id, metaData }) => Promise,
getApiUrl: () => "",
// optional methods
getMany: ({ resource, ids, metaData }) => Promise,
createMany: ({ resource, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
deleteMany: ({ resource, ids, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
updateMany: ({ resource, ids, variables, metaData }) => Promise,
custom: ({ url, method, filters, sort, payload, query, headers, metaData }) =>
Promise,
};
INFORMATION
refine consumes data provider methods using data hooks.
Data hooks are used to operate CRUD actions like creating a new record, listing a resource or deleting a record, etc.
Refer to the Data Provider tutorial for more information and usage examples →
getList required
getList method is used to get a list of resources with sorting, filtering, and pagination features.
It takes resource, sort, pagination, and, filters as parameters and returns data and total.
refine will consume this getList method using the useList or useInfiniteList data hook.
getList: async ({
resource,
hasPagination,
pagination,
sort,
filter,
metaData,
}) => {
const { current, pageSize } = pagination;
const { field, order } = sort;
const { field, operator, value } = filter;
// You can handle the request according to your API requirements.
return {
data,
total,
};
};
TIP
getList also can support cursor-based pagination. Refer to this example for more information.
Parameter Types:
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| resource | string |
| hasPagination? | boolean (defaults to true) |
| pagination? | Pagination |
| sort? | CrudSorting |
| filters? | CrudFilters |
| metaData? | MetaDataQuery |
create required
The create method creates a new record with the resource and variables parameters.
refine will consume this create method using the useCreate data hook.
create: async ({ resource, variables, metaData }) => {
// You can handle the request according to your API requirements.
return {
data,
};
};
Parameter Types
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| variables | TVariables | {} |
| metaData? | MetaDataQuery |
TVariablesis a user defined type which can be passed touseCreateto typevariables.
update required
The update method updates the record with the resource, id, and, variables parameters.
refine will consume this update method using the useUpdate data hook.
update: async ({ resource, id, variables, metaData }) => {
// You can handle the request according to your API requirements.
return {
data,
};
};
Parameter Types:
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| id | BaseKey | |
| variables | TVariables | {} |
| metaData? | MetaDataQuery |
TVariablesis a user defined type which can be passed touseUpdateto typevariables.
deleteOne required
The deleteOne method delete the record with the resource and id parameters.
refine will consume this deleteOne method using the useDelete data hook.
deleteOne: async ({ resource, id, variables, metaData }) => {
// You can handle the request according to your API requirements.
return {
data,
};
};
Parameter Types:
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| id | BaseKey | |
| variables | TVariables[] | {} |
| metaData? | MetaDataQuery |
TVariablesis a user defined type which can be passed touseDeleteto typevariables.
getOne required
The getOne method gets the record with the resource and id parameters.
refine will consume this getOne method using the useOne data hook.
getOne: async ({ resource, id, metaData }) => {
// You can handle the request according to your API requirements.
return {
data,
};
};
Parameter Types:
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| id | BaseKey | |
| metaData? | MetaDataQuery |
getApiUrl required
The getApiUrl method returns the apiUrl value.
refine will consume this getApiUrl method using the useApiUrl data hook.
import { DataProvider } from "@pankod/refine-core";
export const dataProvider = (apiUrl: string): DataProvider => ({
getApiUrl: () => apiUrl,
// ...
});
custom
An optional method named custom can be added to handle requests with custom parameters like URL, CRUD methods, and configurations.
It's useful if you have non-standard REST API endpoints or want to make a connection with external resources.
refine will consume this custom method using the useCustom data hook.
custom: async ({
url,
method,
filters,
sort,
payload,
query,
headers,
metaData,
}) => {
// You can handle the request according to your API requirements.
return {
data,
};
};
Parameter Types
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| url | string |
| method | get, delete, head, options, post, put, patch |
| sort? | CrudSorting |
| filters? | CrudFilters |
| payload? | {} |
| query? | {} |
| headers? | {} |
| metaData? | MetaDataQuery |
Bulk Actions
Bulk actions are actions that can be performed on multiple items at once. Performing bulk actions is a common pattern in admin panels. If your API supports bulk actions, you can implement them in your data provider.
getMany
The getMany method gets the records with the resource and ids parameters. Implementation of this method is optional. If you don't implement it, refine will use getOne method to handle multiple requests.
refine will consume this getMany method using the useMany data hook.
getMany: async ({ resource, ids, metaData }) => {
// You can handle the request according to your API requirements.
return {
data,
};
};
Parameter Types:
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| ids | [BaseKey] | |
| metaData? | MetaDataQuery |
createMany
This method allows us to create multiple items in a resource. Implementation of this method is optional. If you don't implement it, refine will use create method to handle multiple requests.
refine will consume this createMany method using the useCreateMany data hook.
createMany: async ({ resource, variables, metaData }) => {
// You can handle the request according to your API requirements.
return {
data,
};
};
Parameter Types:
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| variables | TVariables[] | {} |
| metaData? | MetaDataQuery |
TVariablesis a user defined type which can be passed touseCreateManyto typevariables.
deleteMany
This method allows us to delete multiple items in a resource. Implementation of this method is optional. If you don't implement it, refine will use deleteOne method to handle multiple requests.
refine will consume this deleteMany method using the useDeleteMany data hook.
deleteMany: async ({ resource, ids, variables, metaData }) => {
// You can handle the request according to your API requirements.
return {
data,
};
};
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| ids | [BaseKey] | |
| variables | TVariables[] | {} |
| metaData? | MetaDataQuery |
TVariablesis a user defined type which can be passed touseDeleteManyto typevariables.
updateMany
This method allows us to update multiple items in a resource. Implementation of this method is optional. If you don't implement it, refine will use update method to handle multiple requests.
refine will consume this updateMany method using the useUpdateMany data hook.
updateMany: async ({ resource, ids, variables, metaData }) => {
// You can handle the request according to your API requirements.
return {
data,
};
};
| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| resource | string | |
| ids | [BaseKey] | |
| variables | TVariables[] | {} |
| metaData? | MetaDataQuery |
TVariablesis a user defined type which can be passed touseUpdateManyto typevariables.
Error Format
refine expects errors to be extended from HttpError.
Here is a basic example of how to implement error handling in your data provider.
import { DataProvider, HttpError } from "@pankod/refine-core";
export const dataProvider = (apiUrl: string): DataProvider => ({
getOne: async ({ resource, id }) => {
try {
const response = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/${resource}/${id}`);
if (!response.ok) {
const error: HttpError = {
message: response.statusText,
statusCode: response.status,
};
return Promise.reject(error);
}
return {
data: response.data,
};
} catch (error) {
const error: HttpError = {
message: error?.message || "Something went wrong",
statusCode: error?.status || 500,
};
return Promise.reject(error);
}
},
// ...
});
Also, Axios interceptor can be used to transform the error from the response before Axios returns the response to your code. Interceptors are methods that are triggered before the main method.
import axios from "axios";
import { DataProvider, HttpError } from "@pankod/refine-core";
import { stringify } from "query-string";
// Error handling with axios interceptors
const axiosInstance = axios.create();
axiosInstance.interceptors.response.use(
(response) => {
return response;
},
(error) => {
const customError: HttpError = {
...error,
message: error.response?.data?.message,
statusCode: error.response?.status,
};
return Promise.reject(customError);
},
);
export const dataProvider = (apiUrl: string): DataProvider => ({
// Methods
});
metaData Usage
When using APIs, you may wish to include custom parameters, such as a custom header. To accomplish this, you can utilize the metaData field, which allows the sent parameter to be easily accessed by the data provider.
TIP
The metaData parameter can be used in all data, form, and table hooks.
Here is an example of how to send a custom header parameter to the getOne method using metaData:
- Send a custom header parameter to the
getOnemethod usingmetaData.
import { useOne } from "@pankod/refine-core";
useOne({
resource: "post",
id: "1",
metaData: {
headers: {
"x-custom-header": "hello world",
},
},
});
- Get the
metaDataparameter from the data provider.
import { DataProvider } from "@pankod/refine-core";
export const dataProvider = (apiUrl: string): DataProvider => ({
...
getOne: async ({ resource, id, variables, metaData }) => {
const { headers } = metaData;
const url = `${apiUrl}/${resource}/${id}`;
httpClient.defaults.headers = {
...headers,
};
const { data } = await httpClient.get(url, variables);
return {
data,
};
},
});
Supported Data Providers
Refine supports many data providers. To include them in your project, you can use npm install [packageName] or you can select the preferred data provider with the npm create refine-app@latest projectName during the project creation phase with CLI. This will allow you to easily use these data providers in your project.
Community ❤️
- Firebase by rturan29
- Directus by tspvivek
- Elide by chirdeeptomar
- Elide GraphQL by chirdeeptomar
- useGenerated by usegen
- Hygraph by acomagu
- Sanity by hirenf14
- SQLite by mateusabelli
- JSON:API by mahirmahdi
- PocketBase by kruschid
- PostgREST by ffimnsr
- Refine SQL X by Seven Du (@medz)
- Refine SQLX by zuohuadong
If you have created a custom data provider and would like to share it with the community, feel free to create a PR. We would be happy to include it on this page for others to use.
Supported Hooks
refine will consume:
getListmethod using theuseListoruseInfiniteListdata hook.createmethod using theuseCreatedata hook.updatemethod using theuseUpdatedata hook.deleteOnemethod using theuseDeleteOnedata hook.getOnemethod using theuseOnedata hook.getApiUrlmethod using theuseApiUrldata hook.custommethod using theuseCustomdata hook.getManymethod using theuseManydata hook.createManymethod using theuseCreateManydata hook.deleteManymethod using theuseDeleteManydata hook.updateManymethod using theuseUpdateManydata hook.
FAQ
How can I create a custom data provider?
How can I customize existing data providers?
How I can override a specific method of Data Providers?
In some cases, you may need to override the method of refine data providers. The simplest way to do this is to use the Spread syntax
For example, Let's override the update function of the @pankod/refine-simple-rest. @pankod/refine-simple-rest uses the PATCH HTTP method for update, let's change it to PUT without forking the whole data provider.
import dataProvider from "@pankod/refine-simple-rest";
const simpleRestProvider = dataProvider("API_URL");
const myDataProvider = {
...simpleRestProvider,
update: async ({ resource, id, variables }) => {
const url = `${apiUrl}/${resource}/${id}`;
const { data } = await httpClient.put(url, variables);
return {
data,
};
},
};
<Refine dataProvider={myDataProvider} />;
- Usage
- Multiple Data Providers
- Methods
- getList
- create
- update
- deleteOne
- getOne
- getApiUrl
- custom
- Bulk Actions
- getMany
- createMany
- deleteMany
- updateMany
- Error Format
- metaData Usage
- Supported Data Providers
- Supported Hooks
- FAQ
- How can I create a custom data provider?
- How can I customize existing data providers?
- How I can override a specific method of Data Providers?